Message Bridging
Enable cross-chain smart contract communication and execution using the Unified Bridge
Overview
Message bridging enables smart contracts on different chains to communicate and execute functions across chains. This allows for complex cross-chain applications where contracts can trigger actions on other chains.
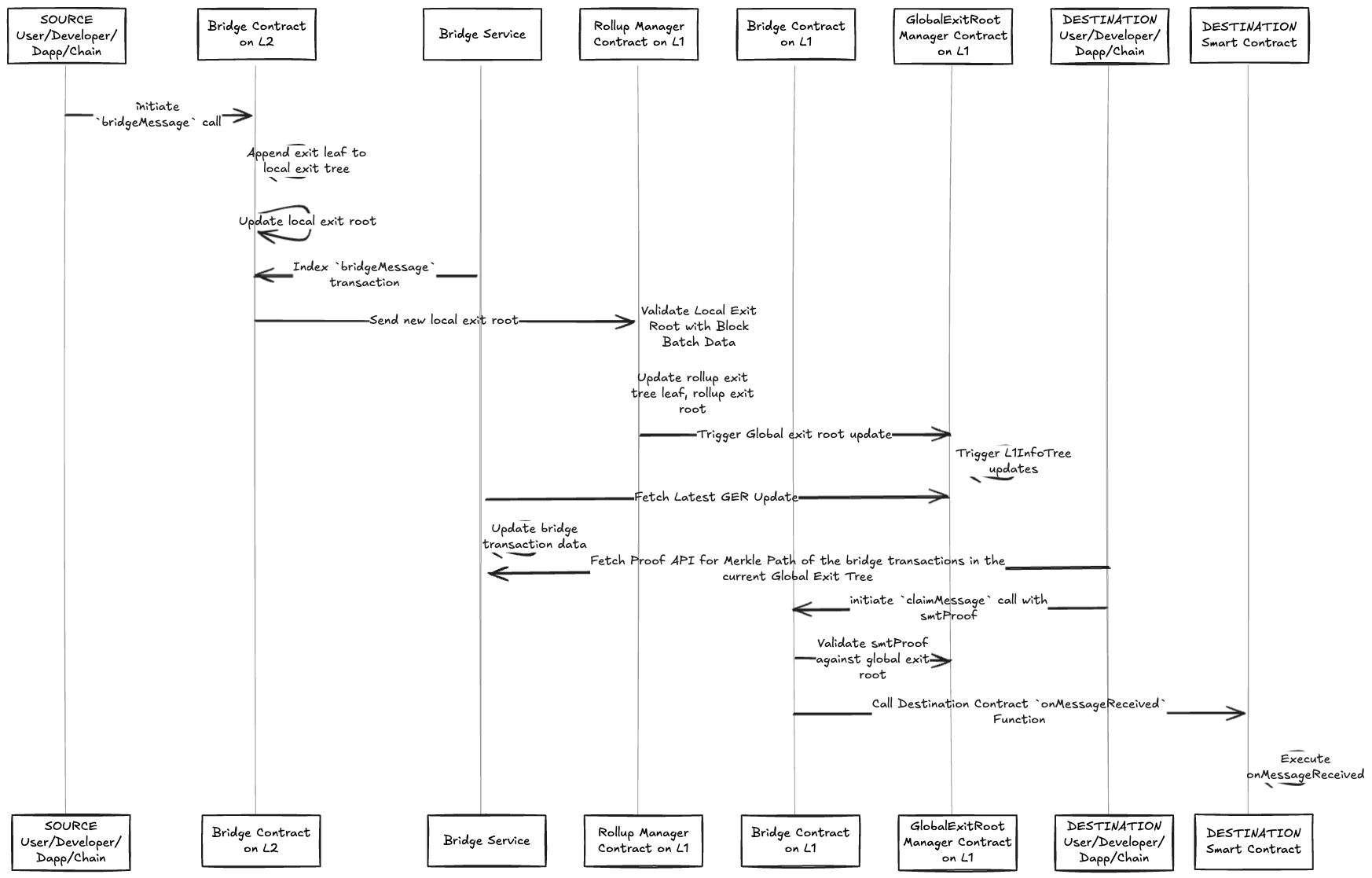
Figure 1: Complete message bridging flow from L2 to L1
Key Concepts
Cross-Chain Execution
Message bridging enables:
- Contract-to-Contract Communication: Smart contracts can call functions on other chains
- Cross-Chain State Updates: Contracts can update state on destination chains
- Complex Workflows: Multi-chain applications with coordinated execution
- Trustless Communication: Cryptographic verification of all cross-chain messages
Message Structure
Cross-chain messages contain:
- Destination Contract: Address of the contract to execute on destination chain
- Function Data: Encoded function call data
- Value: ETH value to send with the message (if any)
- Gas Limit: Maximum gas for execution on destination chain
- Metadata: Additional data for the message
Bridge Message Function
The bridgeMessage function initiates message transfers between chains.
Function Signature
function bridgeMessage(
uint32 destinationNetwork,
address destinationAddress,
uint256 gasLimit,
bytes calldata data
) external payableParameters
destinationNetwork: Network ID of the destination chaindestinationAddress: Address of the contract to execute on destination chaingasLimit: Maximum gas for execution on destination chaindata: Encoded function call data
Process Steps
- Validation: Check destination network is not the source network
- Value Handling: Handle ETH value if provided
- Event Emission: Emit
BridgeEventwith message details - Tree Update: Add message to Local Exit Tree as leaf node
Example Usage
// Bridge a message to call a function on destination chain
bridgeMessage(
1, // destinationNetwork (L2)
0x..., // destinationAddress (contract address)
100000, // gasLimit
abi.encodeWithSignature("updateValue(uint256)", 123) // data
);Claim Message Function
The claimMessage function claims and executes bridged messages on the destination chain.
Function Signature
function claimMessage(
bytes32[_DEPOSIT_CONTRACT_TREE_DEPTH] calldata smtProofLocalExitRoot,
bytes32[_DEPOSIT_CONTRACT_TREE_DEPTH] calldata smtProofRollupExitRoot,
uint256 globalIndex,
bytes32 mainnetExitRoot,
bytes32 rollupExitRoot,
uint32 originNetwork,
address originAddress,
uint32 destinationNetwork,
address destinationAddress,
uint256 gasLimit,
bytes calldata data
) externalParameters
smtProofLocalExitRoot: Merkle proof for Local Exit RootsmtProofRollupExitRoot: Merkle proof for Rollup Exit RootglobalIndex: Global index identifying the messagemainnetExitRoot: Mainnet Exit Root at time of messagerollupExitRoot: Rollup Exit Root at time of messageoriginNetwork: Network ID of source chainoriginAddress: Address that sent the messagedestinationNetwork: Network ID of destination chaindestinationAddress: Address of the contract to executegasLimit: Maximum gas for executiondata: Encoded function call data
Process Steps
- Validation: Verify destination network matches current chain
- Proof Verification: Verify Merkle proofs against Global Exit Root
- Duplicate Check: Ensure message hasn't been claimed before
- Message Execution: Execute the message on destination contract
- Claim Record: Mark message as claimed
Message Execution
// Execute the message on destination contract
(bool success, bytes memory returnData) = destinationAddress.call{
value: msg.value,
gas: gasLimit
}(data);
require(success, "Message execution failed");Important Notes:
- Messages can only be executed if the
destinationAddressis a smart contract that implements theIBridgeMessageReceiverinterface - If the receiving address is an EOA, the call will result as a success, meaning that the amount of ether will be transferred correctly, but the message will not trigger any execution
- If the native gas token is
ETH, then transferETHto thedestinationAddressand execute the message - If
ETHis not the native gas token, then mintWETHto thedestinationAddressand execute the message
IBridgeMessageReceiver Interface
For a contract to receive bridged messages, it must implement the IBridgeMessageReceiver interface:
interface IBridgeMessageReceiver {
function onMessageReceived(
address originAddress,
uint32 originNetwork,
bytes calldata data
) external payable;
}Parameters:
originAddress: Address that sent the message on the source chainoriginNetwork: Network ID of the source chaindata: The message data/metadata sent from source chain
Bridging Flows
L1 to L2 Message Bridging
sequenceDiagram
participant User
participant L1_Bridge as L1 Bridge Contract
participant L1_MET as L1 Mainnet Exit Tree
participant GER_Manager as Global Exit Root Manager
participant L2_Bridge as L2 Bridge Contract
participant L2_GER as L2 Global Exit Root
participant Target_Contract as Target Contract
User->>L1_Bridge: bridgeMessage()
L1_Bridge->>L1_Bridge: Handle ETH value
L1_Bridge->>L1_Bridge: Emit BridgeEvent
L1_Bridge->>L1_MET: Add message to MET
L1_MET->>GER_Manager: Update Mainnet Exit Root
GER_Manager->>GER_Manager: Update Global Exit Root
GER_Manager->>L2_GER: Sync latest GER
User->>L2_Bridge: claimMessage() + proofs
L2_Bridge->>L2_Bridge: Verify Merkle proofs
L2_Bridge->>Target_Contract: Execute message
Target_Contract->>Target_Contract: onMessageReceived()L2 to L1 Message Bridging
sequenceDiagram
participant User
participant L2_Bridge as L2 Bridge Contract
participant L2_LET as L2 Local Exit Tree
participant RollupManager as Rollup Manager (L1)
participant GER_Manager as Global Exit Root Manager
participant L1_Bridge as L1 Bridge Contract
participant Target_Contract as Target Contract
User->>L2_Bridge: bridgeMessage()
L2_Bridge->>L2_Bridge: Handle ETH value
L2_Bridge->>L2_Bridge: Emit BridgeEvent
L2_Bridge->>L2_LET: Add message to LET
L2_LET->>RollupManager: Submit LET to L1
RollupManager->>RollupManager: Update Rollup Exit Root
RollupManager->>GER_Manager: Update Global Exit Root
User->>L1_Bridge: claimMessage() + proofs
L1_Bridge->>L1_Bridge: Verify Merkle proofs
L1_Bridge->>Target_Contract: Execute message
Target_Contract->>Target_Contract: onMessageReceived()L2 to L2 Message Bridging
sequenceDiagram
participant User
participant L2A_Bridge as L2A Bridge Contract
participant L2A_LET as L2A Local Exit Tree
participant RollupManager as Rollup Manager (L1)
participant GER_Manager as Global Exit Root Manager
participant L2B_GER as L2B Global Exit Root
participant L2B_Bridge as L2B Bridge Contract
participant Target_Contract as Target Contract
User->>L2A_Bridge: bridgeMessage()
L2A_Bridge->>L2A_Bridge: Handle ETH value
L2A_Bridge->>L2A_Bridge: Emit BridgeEvent
L2A_Bridge->>L2A_LET: Add message to LET
L2A_LET->>RollupManager: Submit LET to L1
RollupManager->>RollupManager: Update Rollup Exit Root
RollupManager->>GER_Manager: Update Global Exit Root
GER_Manager->>L2B_GER: Sync latest GER
User->>L2B_Bridge: claimMessage() + proofs
L2B_Bridge->>L2B_Bridge: Verify Merkle proofs
L2B_Bridge->>Target_Contract: Execute message
Target_Contract->>Target_Contract: onMessageReceived()Edit on GitHub
Last updated on