Bridge Components
The smart contracts, services, and tools that power the Unified Bridge's cross-chain functionality
Overview
The Unified Bridge consists of three main component categories: on-chain smart contracts, off-chain services, and developer tools. Each component plays a crucial role in enabling secure and efficient cross-chain communication.
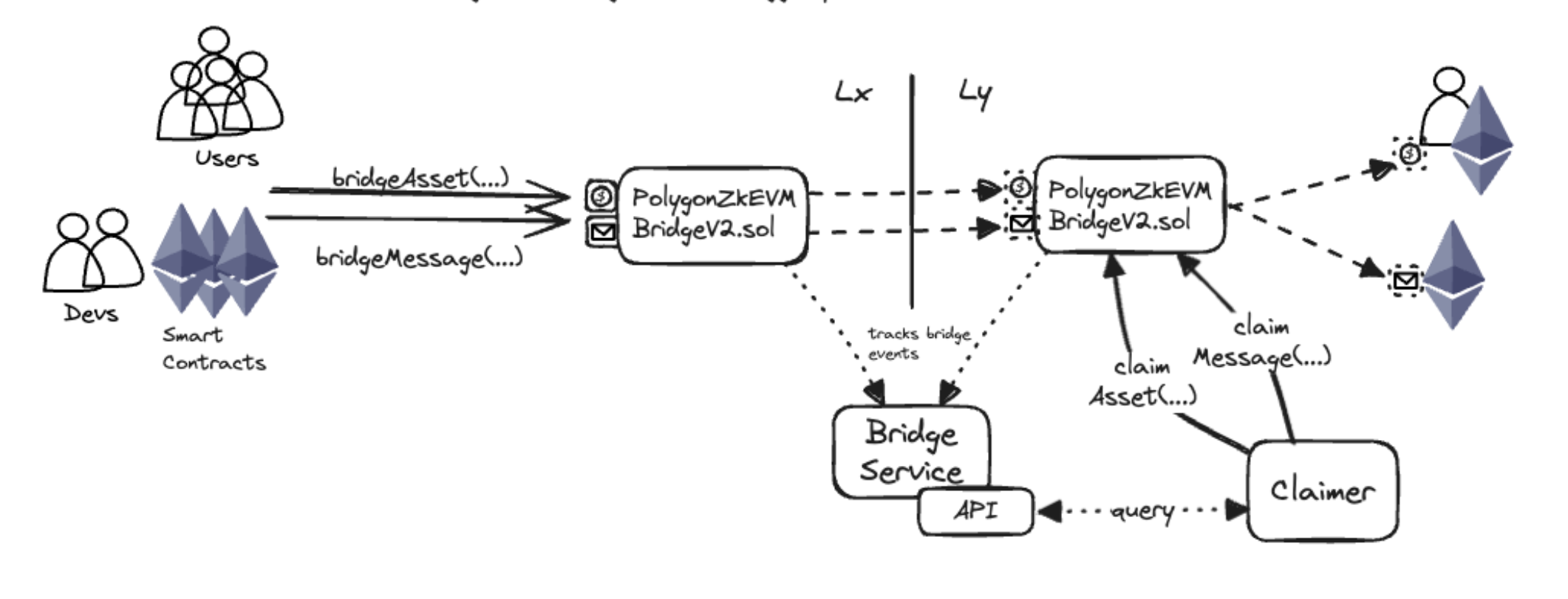
Figure 1: Complete Unified Bridge architecture showing all components and their interactions
Smart Contracts
The core on-chain infrastructure deployed on each connected chain.
PolygonZKEVMBridgeV2.sol
Purpose: Main bridge contract that serves as the interface for all cross-chain transactions.
Key Functions:
-
bridgeAsset(): Initiates asset transfers between chains by validating destination networks, handling different token types (native gas tokens, WETH, ERC20), locking or burning tokens on the source chain, and recording the transaction in the Local Exit Tree. -
bridgeMessage(): Initiates message transfers between chains by packaging message data with optional ETH value, validating gas token conditions, and recording the message in the Local Exit Tree for later execution on the destination chain. -
claimAsset(): Claims bridged assets on the destination chain by verifying Merkle proofs against the Global Exit Root, ensuring the transaction hasn't been claimed before, and transferring or minting the appropriate tokens to the recipient address. -
claimMessage(): Claims bridged messages on the destination chain by verifying Merkle proofs, executing the message on the target contract (if it implementsIBridgeMessageReceiver), and handling ETH/WETH value transfers.
Data Management:
-
Maintains Local Exit Tree (LET) for the chain as a 32-level Sparse Merkle Tree, storing cryptographic commitments of all outgoing bridge transactions and updating the root with each new transaction.
-
Records all outgoing bridge transactions with complete transaction details including destination network, recipient address, token amounts, and metadata, creating an immutable audit trail.
-
Handles complex token operations including locking native tokens in escrow, burning foreign tokens, transferring native ERC20 tokens, and minting wrapped tokens on destination chains based on token origin and type.
Deployment: Deployed on both L1 and all connected L2s
PolygonRollupManager.sol
Purpose: L1 contract that manages rollup state updates and coordinates L2 submissions.
Key Functions:
-
updateRollupExitRoot(): Updates the rollup exit root when L2s submit their Local Exit Roots, validating the cryptographic proofs and ensuring the submitted state transitions are legitimate before updating the aggregated rollup state. -
verifyBatches(): Verifies L2 batch submissions by checking zero-knowledge proofs that demonstrate the validity of state transitions, ensuring that all transactions in the batch were executed correctly according to the L2's rules. -
sequenceBatches(): Sequences L2 batches on L1 by ordering and timestamping batch submissions, providing a canonical ordering of L2 operations that enables deterministic state reconstruction.
Data Management:
-
Maintains Rollup Exit Tree (RET) as a Sparse Merkle Tree where each leaf represents a Local Exit Root from a connected L2, enabling efficient aggregation of all L2 bridge states into a single root hash.
-
Tracks all L2 Local Exit Roots by storing the latest submitted root from each connected chain along with metadata like submission timestamps and batch numbers for audit and synchronization purposes.
-
Updates Global Exit Root when RET changes by automatically triggering updates in the
PolygonZkEVMGlobalExitRootV2.solcontract, ensuring the unified global state reflects all L2 bridge activities.
Deployment: Deployed only on L1
PolygonZkEVMGlobalExitRootV2.sol
Purpose: L1 contract that maintains the Global Exit Root (GER) and L1 Info Tree.
Key Functions:
-
updateGlobalExitRoot(): Updates the Global Exit Root when either the Rollup Exit Root or Mainnet Exit Root changes, computing the new GER ashash(RollupExitRoot, MainnetExitRoot)and appending it to the L1 Info Tree for historical tracking and L2 synchronization. -
getGlobalExitRoot(): Returns the current Global Exit Root that represents the unified state of all cross-chain activities across the entire network, used by L2s for synchronization and by users for generating claim proofs. -
getL1InfoTreeRoot(): Returns the root of the L1 Info Tree which contains all historical Global Exit Roots, enabling L2s to sync with specific historical states and generate valid Merkle proofs for transactions from any point in time.
Data Management:
-
Maintains Global Exit Root (hash of RER and MER) as the single source of truth for the entire network's cross-chain state, automatically recalculating whenever either component root changes to ensure consistency.
-
Maintains L1 Info Tree with historical GERs as a 32-level Sparse Merkle Tree, storing every Global Exit Root update as a timestamped leaf to enable historical state queries and proof generation for past transactions.
-
Provides GER synchronization for L2s by exposing the latest Global Exit Root and L1 Info Tree root, allowing L2 contracts to fetch and verify the current unified state for processing incoming cross-chain claims.
Deployment: Deployed only on L1
PolygonZkEVMGlobalExitRootL2.sol
Purpose: L2 contract that synchronizes with L1 Global Exit Root updates.
Key Functions:
-
updateExitRoot(): Syncs with the latest Global Exit Root from L1 by calling the L1 Global Exit Root contract, fetching the current GER and L1 Info Tree root, and updating the L2's local copy to enable validation of incoming cross-chain claims. -
getGlobalExitRoot(): Returns the current synchronized Global Exit Root stored on this L2, which is used by the bridge contract to verify Merkle proofs during claim operations and ensure claims are based on the latest global state. -
getL1InfoTreeRoot(): Returns the synchronized L1 Info Tree root that corresponds to the current Global Exit Root, enabling the L2 to validate that claim proofs are based on legitimate historical states from the L1 Info Tree.
Data Management:
-
Maintains synchronized copy of L1 GER by periodically fetching updates from the L1 Global Exit Root contract and storing them locally, ensuring the L2 has the latest unified network state for claim verification.
-
Maintains synchronized copy of L1 Info Tree root along with the corresponding Global Exit Root, creating a consistent state snapshot that enables proper validation of Merkle proofs during cross-chain claim operations.
-
Enables L2 to verify cross-chain claims by providing the necessary Global Exit Root and L1 Info Tree root data that the bridge contract uses to validate Merkle proofs and ensure claimed transactions were properly settled on L1.
Deployment: Deployed on all connected L2s
Bridge Service
Off-chain infrastructure that provides indexing, APIs, and proof generation services.
Chain Indexer Framework
Purpose: EVM blockchain data indexer that parses and organizes blockchain data.
Key Features:
-
Real-time Indexing: Continuously monitors the blockchain for bridge-related events by subscribing to new blocks and scanning for
BridgeEventandClaimEventlogs, ensuring that all cross-chain transactions are captured immediately as they occur. -
Data Parsing: Extracts and structures bridge transaction data from raw blockchain logs, converting hex-encoded event data into structured formats that include transaction details, token information, addresses, amounts, and timestamps.
-
Event Processing: Processes
BridgeEventlogs (emitted during bridging) andClaimEventlogs (emitted during claiming) to track the complete lifecycle of cross-chain transactions from initiation to completion. -
Database Storage: Stores indexed data in structured databases optimized for API queries, enabling fast retrieval of transaction history, status updates, and proof generation data for user interfaces and applications.
Deployment: One instance per connected chain
Technology: Built on Polygon's Chain Indexer Framework
Transaction API
Purpose: Provides real-time bridge transaction status and details for user interfaces.
Key Endpoints:
- Testnet:
https://api-gateway.polygon.technology/api/v3/transactions/testnet?userAddress={userAddress} - Mainnet:
https://api-gateway.polygon.technology/api/v3/transactions/mainnet?userAddress={userAddress}
Response Data:
- Transaction status (pending, completed, failed) with real-time updates as transactions progress through the bridging and claiming phases
- Token details including contract addresses, transfer amounts, token symbols, and decimals for accurate display in user interfaces
- Source and destination chain information including network IDs, chain names, and block numbers where transactions were processed
- Timestamps for transaction initiation, L1 settlement, and claim completion to track transaction lifecycle timing
- Deposit count (Local Exit Tree index) required for Merkle proof generation during the claim process
Authentication: Requires API key in request header
Example Usage:
curl --location 'https://api-gateway.polygon.technology/api/v3/transactions/mainnet?userAddress=0x...' \
--header 'x-api-key: <your-api-key-here>'Proof Generation API
Purpose: Generates Merkle proofs required for claiming bridged assets and messages.
Key Endpoints:
- Testnet:
https://api-gateway.polygon.technology/api/v3/proof/testnet/merkle-proof?networkId={sourceNetworkId}&depositCount={depositCount} - Mainnet:
https://api-gateway.polygon.technology/api/v3/proof/mainnet/merkle-proof?networkId={sourceNetworkId}&depositCount={depositCount}
Parameters:
-
networkId: Network ID registered on Agglayer that identifies the source chain (0 for Ethereum/Sepolia, 1 for Polygon zkEVM/Cardona, etc.), used to determine which Local Exit Tree contains the transaction. -
depositCount: The leaf index from the source chain's Local Exit Tree (obtained from Transaction API response), which specifies exactly which transaction leaf to generate proofs for.
Response Data:
-
smtProofLocalExitRoot: Merkle proof demonstrating that the specific transaction exists in the source chain's Local Exit Tree, providing the cryptographic path from the transaction leaf to the Local Exit Root. -
smtProofRollupExitRoot: Merkle proof demonstrating that the source chain's Local Exit Root exists in the Rollup Exit Tree on L1 (only needed for L2 to L1/L2 transactions), proving the L2's state was properly submitted to L1. -
globalIndex: The 256-bit Global Index that uniquely identifies this transaction within the entire network, encoding the source network type, rollup ID, and local index information. -
mainnetExitRoot: The Mainnet Exit Root at the time this transaction was processed, used for constructing the Global Exit Root during claim verification. -
rollupExitRoot: The Rollup Exit Root at the time this transaction was processed, used for constructing the Global Exit Root during claim verification.
Authentication: Requires API key in request header
Auto Claim Service (only on L2s)
Purpose: Automated service that claims bridged transactions on destination chains.
Key Features:
-
Automatic Claiming: Continuously monitors for claimable transactions across all connected chains by querying the Transaction API, detecting when transactions are ready to be claimed (L1 finalized), and automatically executing claim transactions to complete the cross-chain transfer.
-
Gas Optimization: Optimizes gas usage for claim transactions by batching multiple claims together when possible, using dynamic gas pricing based on network conditions, and implementing efficient claim strategies to minimize transaction costs.
-
Error Handling: Handles failed claims gracefully by implementing retry mechanisms with exponential backoff, logging detailed error information for debugging, and providing fallback strategies when primary claim methods fail.
-
Monitoring: Provides comprehensive monitoring and alerting for claim operations including success/failure rates, processing times, gas usage statistics, and automated notifications when manual intervention is required.
Deployment Options:
-
DApp Integration: Deploy as part of your dApp infrastructure to provide seamless auto-claiming for your users, improving user experience by eliminating manual claim steps and reducing friction in cross-chain workflows.
-
Chain Integration: Deploy as a chain-level service where the L2 operator runs the claiming service for all users, providing a public good that improves the overall user experience on that chain.
-
Standalone Service: Deploy as an independent claiming service that can serve multiple dApps or chains, potentially monetized through small fees or operated as a community service.
Configuration:
- Source and destination chain RPC URLs for monitoring bridge events and submitting claim transactions across all supported networks
- Bridge contract addresses for each supported chain to interact with the correct bridge instances
- Private keys for claiming with appropriate security measures and key rotation policies
- Gas price settings including maximum gas prices, priority fees, and dynamic pricing strategies based on network congestion
Last updated on